Every year when the budget is presented, people wait for new announcements on income tax. A lower tax outgo doesn’t harm anyone. Either the government is expected to increase the income slab rate that is exempted from paying taxes or offer more tax deductions. The government allows several types of deductions to the citizens for a variety of reasons such as boosting consumption or promoting investment in a certain type of instruments.
When the date to file income tax returns nears, a mad scramble for tax-saving begins. An annual income of Rs 5 Lakhs is effectively tax-free in the country. After the limit is breached the best way to save taxes is to use deductions, which decreases the taxable income. Income tax deductions have become synonymous with Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. An individual can claim a deduction of Rs 1.5 lakhs in a year under Section 80C for investments in financial instruments like tax-saving fixed deposits, PPF and EPF. Besides Section 80C, there are several other sections that are relevant to you.
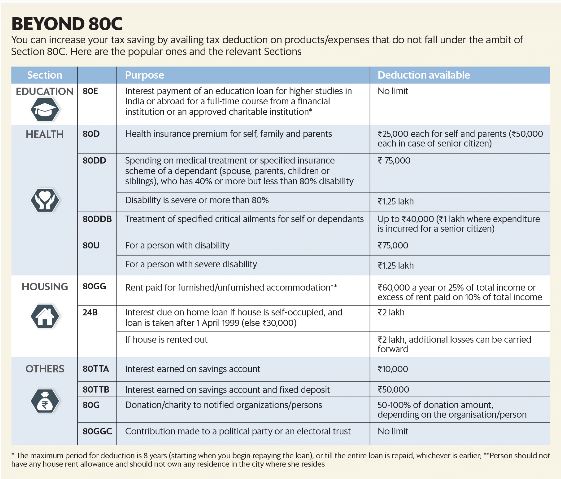
Medical expenses are rising rapidly in the country and in the absence of medical cover you may have to dip into your savings to pay for health issues. Having a health insurance policy is a must. The premiums paid for health insurance qualify for deduction under Section 80D of the income tax act. A maximum deduction of Rs 25000 is allowed every year on the premium paid for health insurance for self and family. The limit for senior citizens is Rs 50,000 per financial year. Apart from premiums paid, an additional deduction of Rs 5000 is allowed for health check-ups. The Rs 5,000 is included within the overall deduction limit of Rs 25,000.
Source: fingyan.com
Quality education is not cheap, but a personal loan for education can help you fulfil your dream. Interest paid on education loan is eligible for deduction under 80E. Deduction for interest paid on education loan can be claimed for eight consecutive years. It should be noted that the deduction is only for the repayment of interest and not the principal amount.
The National Pension Scheme has become the savings instrument of choice for many due to the various tax benefits it offers. NPS is a market-linked scheme and is likely to generate decent returns in the long term. You can choose to allocate your funds to equity or debt instruments. Besides, returns, it also offers many tax benefits. You can avail an additional deduction of Rs 50,000 under Section 80CCD (1b).for investing in NPS.
Owning a house is a lifelong dream for many people. People often avail home loan to fulfil their dreams. Both the principal and interest paid on a home loan taken to buy or construct a house qualify for deduction under separate sections. The principal paid qualifies for deduction under Section 80C, and the interest paid, in case of a self-occupied house, under Section 24(b), with a limit of Rs 2 lakhs.
The government has allowed a deduction for charitable donations under Section 80G. Donations to certain charitable institutions and relief funds are eligible for deduction. The amount of deduction allowed varies depending on the institution and the section under which it is registered. For instance, a donation to the Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund qualifies for 100 percent deduction. However, donations above a certain limit do not qualify for a deduction.
Source: Livemint
Deduction under Section 80DD is allowed to individuals or HUFs for a dependent who is differently-abled and is wholly dependent on them. This deduction can be claimed by the person who has incurred expenses for the dependent differently-abled person. The amount of deduction under the section depends on the percentage of disability.
Most people don’t know but the interest earned on the savings account too is eligible for deduction. The section covers interest income from savings account in banks, cooperative banks and post offices. The maximum deduction allowed under Section 80TTA is Rs 10,000 in a financial year. The section does not cover interest from fixed deposits or recurring deposits.
The government does not have to necessarily tinker with tax exemption limits to provide tax relief to citizens. The numerous deductions allowed help reduce the tax burden on people. Sometimes deductions under various sections overlap with each other and one should very carefully file his/her income tax returns every year.
Quick Links





