Learn what a Fair Value Gap is in technical analysis and how traders use it to identify potential areas of price imbalance and reversal.
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a popular price-action concept used by traders to identify market imbalances where price has moved too quickly, leaving behind inefficient trading zones. These gaps are areas where price has historically revisited, indicating potential zones of interest in price analysis. Fair Value Gaps are widely used in institutional trading concepts and are especially common in forex, indices, and equity markets. Understanding FVGs helps traders improve entries, exits, and overall market timing.


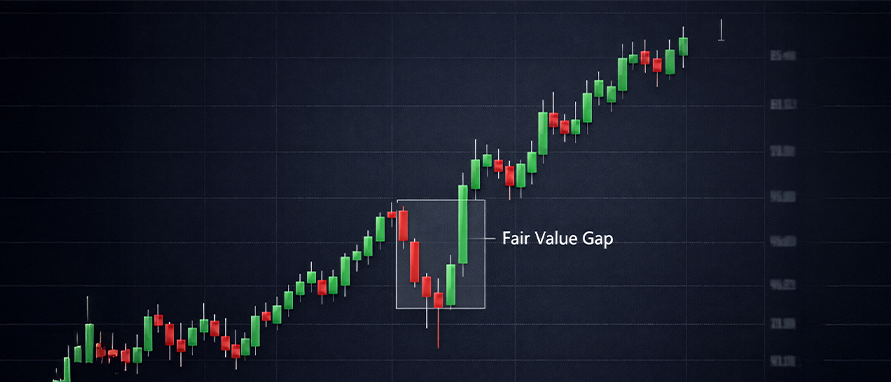
.jpeg)






